Stitching together a better life
The unique sewing skills and designs of the Huayao people are helping mountain villages in Hunan overcome poverty while breathing new life into their culture, Li Yingxue and Feng Zhiwei report.
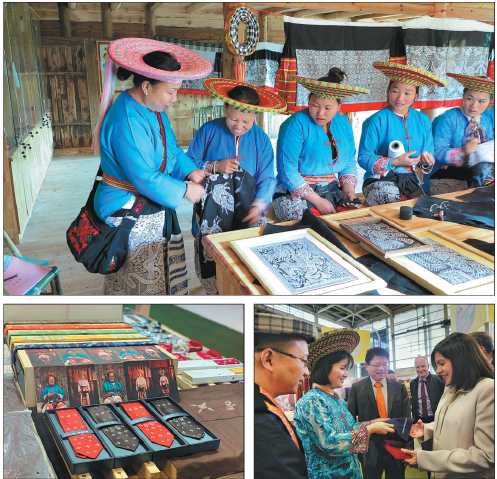
Almost every Huayao woman can do tiaohua, or cross-stitching, and each piece embodies its maker's own understanding of, and reflections on, life.
The Huayao people are an ancient branch of the Yao ethnic group. Huxingshan Yao town is home to around 7,000 Huayao people, but it was also one of the most impoverished and remote towns in Longhui county, Shaoyang, Hunan province.
For the best part of a decade, a team from Hunan University has been helping Baishuidong village in the town to overcome poverty and inherit the cross-stitching skill by promoting its cultural and creative products and boosting local tourism, trying to put the small village on the map.
Yang Min, the head of the town, says, "The goal has changed from poverty alleviation to overcoming poverty, which inspires our villagers, and it is the most precious treasure that Hunan University leaves us."
There is no written language for the Huayao people who live in remote mountain settlements, so it's difficult to save its ethnic culture.
The skill of the Huayao's cross-stitch work, which has a history stretching back a thousand years, fills the gap to some extent-it has played an important role in inheriting Huayao culture and recording the history of the Huayao people.
However, the new generation of Huayao women yearn for more urban fashions. Some of them do not wear their traditional outfits anymore and there is a lack of passion for the needlework.
Making a set of traditional Yao clothes requires heavy needlework-a skirt, alone, needs at least 300,000 stitches and it takes a master of the craft between six and 12 months to complete.
Many Huayao women shy away from the craft because of the complicated needlework, and another challenge for Huayao cross-stitch work is that it's not easy to get onto the market.
The poverty alleviation team from Hunan University began helping in Baishuidong village in 2012. When they first arrived, they eyed the Huayao cross-stitch work as a potential revenue stream.
They formed a design team to develop cultural and creative products based on intangible cultural heritage projects, including Lunar New Year paintings and the cross-stitching skills of Huayao people.
As well as the more than 140 cultural and creative products the team designed, they also established a stitching design studio for tiaohua and an exhibition space for Huayao culture.
"We used to just design special packaging for local products, but that doesn't add value to the products themselves, and is neither sustainable nor recyclable," Wang Xile, a member of the team, recalls.
When she came to Baishuidong several years ago as a bachelor student majoring in visual communication, she was attracted by the unique Huayao cross-stitching skill.
After spending time in the village, she decided to set the research direction of her master's study toward the inheritance and protection of intangible cultural heritage.
"Now, we want to innovate and make a collaborative effort to change. We are responsible for understanding the customers' requirements with regard to the quantity and the sizes," Wang says. "Then we let the women create the patterns they see fit, so that each product is unique."
Yang Liaohua, a villager from Baishuidong, draws a small income from growing honeysuckle. The Hunan University's team reached out to her and asked an inheritor of Huayao cross-stitch to teach her the skill for free.
Yang learned very quickly and the needlework now brings her an extra income of more than 10,000 yuan ($1,550) each year.
The team also developed an app to educate children about the Hauyao cross-stitch skill and Huayao culture.
"The women use colorful threads to make many small cross-stitches that form bigger patterns and create unique pieces of work, but regarding the inheritance of the skill, there are many difficulties, such as the language barrier," Wang says.
"So, we want to design a game to let the children learn about Huayao culture and the cross-stitch skills by raising their interest and lowering the difficulty," Wang says, adding that the inspiration to create the app came from her field research in Longhui county.
According to Zhang Duoduo, associate professor at Hunan University's School of Design, as well as developing the app for preschool children, their team is also designing a board game about Huayao culture.
"People are the key to inheriting intangible cultural heritage, and our idea is to develop digital education products which are designed to attract users from an early age," Zhang says.
She hopes to take Baishuidong as a starting point and expand this model of combining the creative inheritance methods and art education with intangible cultural heritage to all the impoverished regions in China with children who are left behind by parents seeking work elsewhere.
In 2018, the results of their team's study on Huayao cross-stitch in Southwest China was presented at the 20th International Conference on Human-Computer Interaction held in Las Vegas in the United States, and was also recommended at the 2018 Internet Yuelu Summit in Hunan.
There have been 70 designers from seven countries who have developed creative and cultural products around Lunar New Year paintings and the Huayao cross-stitch. In 2017, those products yielded a revenue of more than 6 million yuan.
Huxingshan Yao town also takes full advantage of its cultural resources to develop its tourism, which provides a path to overcome poverty and achieve prosperity.
In 2008, Huayao folk songs from Longhui county and the traditional cross-stitch were added to the national intangible cultural heritage list.
Cultural heritage provides unique tourism resources for the village, such as the colorful wedding customs of the Huayao people.
In 2020, a summer culture and tourism festival took place in Longhui county to draw attention to the cultural heritage of the many villages in Hunan province.
The infrastructure in the town, including the roads, houses and electric power grid, keeps improving, as do local public services, such as education and medical facilities. The town has become a model "beautiful village" and has been attracting a growing number of tourists.
Contact the writers at liyingxue@chinadaily.com.cn